 The RAID level concept was placed in 1988 and it was categorized in 6 levels from 0 to 5. This allowed the levels of proper versions based on numbers and how they can be utilized based on the redundancy level and distribution of data across the storage array. RAID configurations are helped a lot in saving money and providing redundancy. With upcoming advancements in technology, these RAID levels are combined and formed nested RAID levels.
The RAID level concept was placed in 1988 and it was categorized in 6 levels from 0 to 5. This allowed the levels of proper versions based on numbers and how they can be utilized based on the redundancy level and distribution of data across the storage array. RAID configurations are helped a lot in saving money and providing redundancy. With upcoming advancements in technology, these RAID levels are combined and formed nested RAID levels.
Mostly the RAID levels are divided into two parts.
1. Standard RAID levels
2. Nested RAID levels
Standard RAID levels
Here will talk about mostly used RAID configurations.
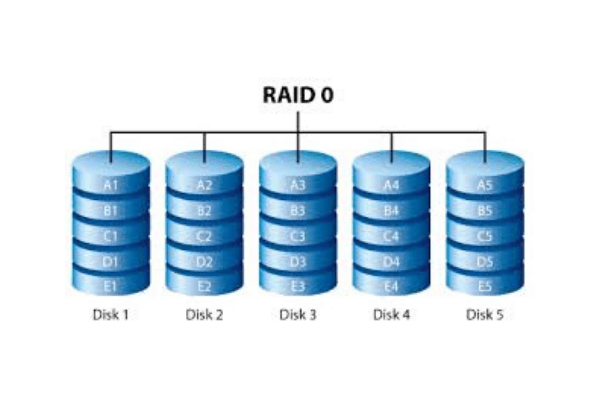
RAID 0:
This level uses striping to distribute the data across the storage array but there is no redundancy. This doesn’t provide fault tolerance but the performance is best.
RAID 1:
This level provides disk mirroring and this configuration requires at least two drives. One drive for storing the data and other drives for mirroring the same data. The drives should be of the same size. This performs well while reading the data but doesn’t perform well while writing the data. It performs writing performance on a single disk at a time.
RAID 5:
This level uses block-level striping parity configuration. This parity information is distributed across each drive which allows the availability of data even if one drive fails. This can sustain the failure of a maximum of 2 drives and required at least 3 disks to configure RAID 5. This doesn’t give high performance as compared to RAID 0. This is recommended to use at least 5 disks for configuring RAID 5 and it helps to get somewhat better performance.
This configuration will be a poor selection for write-intensive systems because this performance will impact associated with writing parity information. If any disk fails then it will take a long time to rebuild. The performance will be degrading while rebuilding the array and this will make the array vulnerable for other disks to fail during this time.
RAID 6:
This is as same as the RAID 5 configuration. The only difference is it includes a second parity scheme that is distributed across the drives in the array. This raid level uses additional parity which allows the array.
Nested RAID levels
These are a combination of 2 different RAID levels and thus create a nested RAID level. Some of them are illustrated below:
RAID 10 (RAID 1+0):
This is a combination of RAID 1 and RAID 0 and this is referred to as RAID 10. This offers higher performance in terms of striping of data in RAID 0 and mirroring the data using RAID 1. But this arrangement is expensive to implement. In this level, the data is mirrored and then stripped. many hard drives are required.
RAID 50 (RAID 5+0):
RAID 5+0 uses the distributed parity and then striping it using RAID 0 which improves the performance without reducing data protection.
Benefits of RAID
By combining multiple hard drives together RAID can improve the work of a single drive and also depending on the configuration it can also boost the performance of the servers and provides reliability on the crashing of hard drives.
Different RAID levels provide different types of functionality. They provide high performance in terms of reading and writing (I/O). It also provides redundancy and data security. By using lower-priced disks in large numbers RAID configurations can provide good results.


