Redundant Arrays of Inexpensive Disks (RAID), is an array of inexpensive drives that could help in increasing the performance of the storage system. An array of disks could be more reliable than anyone disk drive. The RAID concept helped stimulate the data storage market to develop more RAID array products. Later on, the term inexpensive was replaced with independent by industry vendors as it was low in cost.
How RAID concept works?
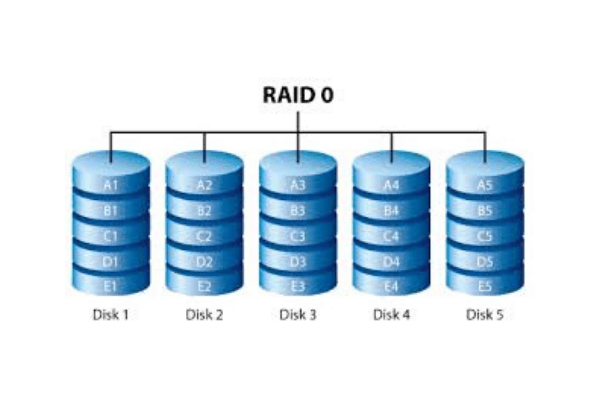
The RAID concept works by distributing data on multiple disks and allowing input/output (I/O) operations to overlap in a balanced way. This also helps improving performance because the use of multiple disks increases the mean time between failures (MTBF). This also increases fault tolerance.
Disk arrays appear as a single logical hard disk to the operating system (OS). RAID implements the techniques of disk mirroring or disk striping. In mirroring the data is copied onto more than one drive. RAID concept combines disk mirroring and disk striping on a RAID array. Mirroring and striping are used together in nested RAID levels.
RAID Controller
A RAID controller is a kind of bridge between an Operating System and a hard disk. These hard drives can be an array of disks combined together to form a single logical disk. RAID controller can improve input/output performance and also helps to protect data in case of hardware failure or crash.
This controller is available in hardware and software-based. In a hardware-based RAID a physical RAID controller box is connected with the server that manages multiple storage arrays. This is available in the form of Peripheral Component Interconnect or PCI Express card and designed to support different drive formats like SATA and SCSI. Sometimes an RAID controller can also be integrated into motherboards.
In software RAID software is used to control the storage arrays but it will use the resources from the hardware. Although it performs the same function but it doesn’t provide the same performance compared to hardware-based RAID controller.
In some motherboards, the RAID controller is already integrated and has a firmware-based chip. In this kind of arrangement, all the operations are performed by CPU which is similar to software RAID operation. At the beginning of the boot sequence this RAID system is implemented. After loading the operating system, the controller driver takes the command for RAID functionality. Firmware RAID controllers are less expensive compared to hardware controllers but they put more strain on servers processor. This kind of arrangement is also known as hardware-assisted software RAID, hybrid model RAID, and fake RAID.
Problems in using RAID
There are many RAID configurations available but they are very expensive. Combining different RAID levels and creating nested RAID is more expensive than traditional RAID levels. Nested RAID required a number of disks. The cost increases per GB of storage because most of the drives are used for redundancy and data backup. Nested RAID configuration has become more popular these days in spite of cost involvement as they provide a very good reliability and performance as compared to traditional RAID levels.
At the beginning, all the drives in a RAID are installed at the same time which makes the age, operating conditions, and same wear tear. When one drives fail then there is a high possibility of failure of other drives soon. Disk failures can be tolerated by nested RAID levels as they provide a higher degree of redundancy. In some nested RAID levels, it can sustain 2 disk failures.