Digital Communications includes the laws and regulations that enable the exchange of information between computers with various operating systems, languages, cabling, and locations. This online course with its principles and algorithms shows you the fundamentals of Data Processing and Computer networks.
What is a Computer Network?
A computer network is a community of two or more computer systems that are interconnected. A network link may be built utilizing either cable or wireless devices.
Each network is composed of hardware and software which connects computers and devices.
You’ll read in this guide on Software Networking concepts:
Advantages of a Computer Network
These are the main advantages/pros of utilizing computer networking:
- It helps you connect to several machines to transmit and receive information as you use the network together.
- It helps you to share printers, scanners, and email.
- Helps you to share information at very fast speed
- Electronic communication is less expensive and more effective than without the network.
Computer Network Components
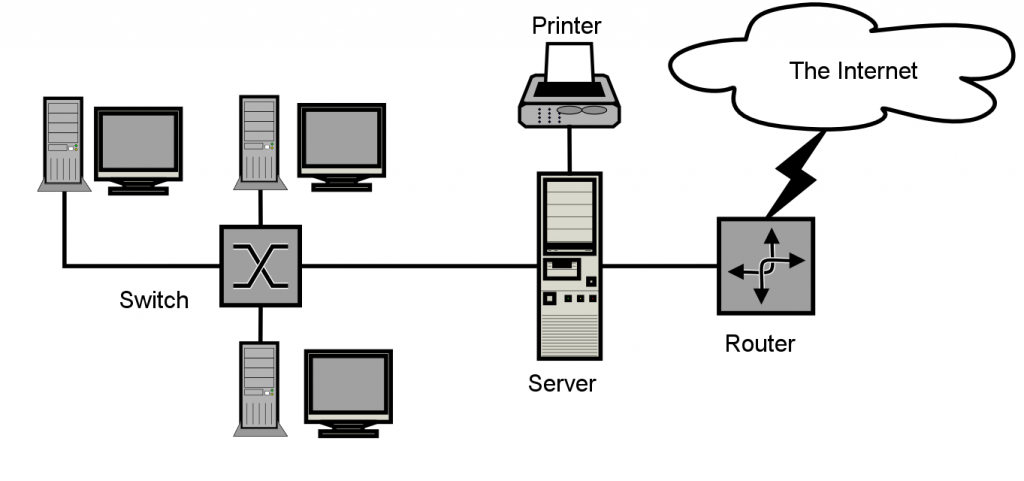
Switches: Switches act as a router that links machines, printers, and other hardware equipment to a campus or building network.
This helps computers to connect on the network, as well as with other networks. It lets you distribute the capital and lower each organization’s expense.
Routers: Routers help you connect to several networks. It helps you to link multiple computers with a single internet connection and saves energy. This networking part functions as a dispatcher, enabling you to examine transmitted data through a network. It picks the best path for moving data automatically and sends it on its way.
Servers: Servers are machines that contain network operating systems, mutual applications, archives, and. The servers give all network users access to network services.
Clients: Clients are electronic machines that navigate the network and utilize it, as well as exchange network services. They also network customers, because they can submit and receive application requests.
Transmission Media: Transmission media is a carrier used to link networked devices, such as coaxial cable, twisted-pair tube, and optical fiber cable. Often named connections, pipes, or boards.
Access points: Access points enable the devices to connect without cables to the wireless network. A cellular network allows you to carry new apps, which offers smartphone customers with reliable assistance.
Shared Data: Shared data is data exchanged by clients such as data files, access programs for printers, and email.
Network Interface Card: Network Interface module sends, collects, and monitors the movement of data between the device and the network.
Local Operating System: A central operating system that lets personal computers navigate data, prints to a nearby printer, and utilizes one or more disk and CD drives stored on your machine.
Network Operating System: An operating network framework is a software that operates on computers and servers. It lets the machines connect across the network.
Protocol: A protocol is the collection of specified rules requiring two individuals to interact over the network. Any common protocols that are used to this end are IP, TCP, UDP, FTP, etc.
Hub: Hub is a system that breaks access to a network into several computers. It serves as a processing center and it transfers the request via a cable to the hub if a device demands some input from a machine or the network. The center must accept the message and pass it out to the entire network.
LAN Cable: Cable Local Area Network(LAN) is sometimes called Ethernet or network cable. This is used to link a computer to the Internet.
OSI: OSI calls for Open Interconnection Infrastructure. This is a guide model that lets you define communications requirements.
Uses of Computer Networks
Here are some common application of computer networks
- Helps you share tool like printers
- Requires you to exchange costly tools and archive with Network participants
- Provides quick and reliable connectivity from one device to the next
- It helps you to share information and data between users over a network.
Disadvantages of using Computer Networks
Here are drawbacks/ cons of using computer networks:
- Hardware and device expenditure may be costly for initial set-up
- If you do not take appropriate protection measures, such as file encryption, then firewalls will place your data at risk.
- Such network architecture devices will not survive for several years, so it may become obsolete or malfunctioning, and need to be replaced.
- Needs room for smooth administration
- Frequent software errors and cable drops
What Are the Important Types of Computer Networks?
There are various forms of computer networks. We may categorize them both in terms of their scale and function.
The complexity of a network will be expressed in the geographic region and the number of machines that are part of its networks. This involves products that are located in one space and distributed to millions of devices
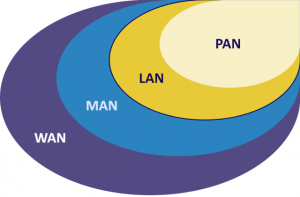
Some of the most popular network types are:
- PAN
- LAN
- MAN
- WAN
What is PAN (Personal Area Network)?
PAN is a network of computers clustered around an individual. It usually consists of a remote assistant, a device, a smartphone, or a person. PAN may be used to create contact with such personal computers to link to a wireless network and the Internet.
Characteristics of PAN
- This is mainly a network of personal computers installed inside a small area.
- Requires you to manage The computer interconnection within a single user’s surroundings.
- PAN incorporates handheld computers, phones, and notebooks.
- It can be linked wirelessly to WPAN, the internet.
- PAN-enabled appliances: cordless controllers, buttons, and Bluetooth devices.
Advantages of PAN
Here, are important pros/benefits of using PAN network:
- PAN networks are comparatively stable and reliable
- It just provides short-range options up to 10 meters
- Strictly confined to a small field
Disadvantages of PAN
Here are important cons/ drawback of using PAN network:
- At the same radio bands, it may create a bad link to other networks.
- Distance limits.
What is LAN?
A Local Area Network (LAN) is a collection of machine and peripheral devices that are linked to a small region such as education, study, house, and office buildings. It is a commonly used network for exchanging services such as data, printers, sports, and the like. The easiest form of the LAN network is to link somebody’s home or office with computers and a printer. In general, the LAN is used as one form of medium of transmission.
It is a network that comprises less than 5000 interconnected computers through several buildings.
Characteristics of LAN
Here are important characteristics of a LAN network:
- It is a private network, thus, it is rarely regulated by an outside regulatory agency.
- Compared to other WAN networks LAN runs at a comparatively higher speed.
- Internet access management mechanisms such as token ring and ethernet operate in various forms.
Advantages of LAN
Here are pros/benefits of using LAN:
- Computer services such as hard disks, DVD-ROMs, and printers can share networks in the local region. This reduces the expense of electronics transactions considerably.
- Because of purchasing the approved program for each device in the network, you will use the same program across the network.
- Data of all network users can be maintained on the host computer’s single hard disk.
- The data and communications can be quickly transmitted via networked machines.
- Managing data at just one location would be simple, which allows data more stable.
- Local Area Network offers the facility for the exchange of a common Internet link for all LAN users.
Disadvantages of LAN
Here are the important cons/ drawbacks of LAN:
- LAN will potentially save money thanks to mutual computing space, but the overall deployment expense of Local Area Networks is very high.
- The LAN administrator will search any LAN user’s data files and this does not have sufficient protection.
- Unauthorized users can access an organization’s essential data in case LAN admin is unable to protect a centralized repository of data.
- Local Area Network needs continuous LAN maintenance because there are device setup and equipment failures
Also, See What is LAN and WAN? | How it works?
What is WAN?
WAN (Wide Area Network) is another big computer network that is distributed across a vast geographic region. WAN network device may be a LAN interface that utilizes telephone lines and radio waves to communicate with other LAN’s. This is often restricted to an agency or a company.
Characteristics of LAN:
- The program files are exchanged by all users; thus, the new data are open to everyone.
- Any organization will use WAN to shape its interconnected global network.
Advantages of WAN
Here are the benefits/ pros of using WAN:
- WAN lets you reach a wider geographic region. Company offices situated at greater distances thus can connect effectively.
- It contains items such as smartphones, a desktop, laptops, servers, consoles for games, etc.
- Wi-Fi communications operate with wireless transmitters and receivers built-in client computers.
Disadvantage of WAN
Here are drawbacks/cons of using WAN:
- Investment costs for initial configuration are very high.
- Maintaining the WAN network is difficult. Expert technicians and network administrators are needed.
- Because of the broad scope and the usage of various techniques, there are further mistakes and problems.
- With the presence of various wired and wireless systems, it requires more time to resolve issues.
- It offers fewer protection as opposed to other network types.
What is a MAN?
A Metropolitan Area Network or MAN consists of a computer network in an entire area, college campus, or a regional city. This form of network is bigger than a LAN, often restricted to a single building or location. This kind of network helps you to span a region from few miles to tens of miles, depending on the kind of setup.
Characteristics of MAN
Here are important characteristics of the MAN network:
- It includes primarily towns and cities within a maximum radius of 50 km
- The method most commonly used is optical fiber, cables
- Proper data levels for distributed computing systems.
Advantages of MAN
Here are pros/benefits of using MAN system:
- It offers easy connectivity with high-speed networks such as fiber-optic cables.
- It offers outstanding support for a wide network of sizes and better exposure to WANs.
- The dual bus in MAN network offers space for simultaneous data transfer in both directions.
- A MAN network covers only those parts of a city or a whole region.
Disadvantages of MAN
Here are drawbacks/ cons of using the MAN network:
- To build a MAN link from one place to another you need more cable.
- It is hard to render the device safe from hackers in the MAN network
Other Types of Networks
- WLAN (Wireless Local Area Network)
- Storage Area Network
- System Area Network
- Home Area Network
- POLAN- Passive Optical LAN
- Enterprise private network
- Campus Area Network
- Virtual Area Network
Let’s see all of them in detail:
1) WLAN
Wireless Local Area Network (WLAN) lets you link single or numerous devices using wireless networking within a small environment, such as a house, school, or office building. It allows consumers the freedom to travel about within a particular region of coverage that can link to the network. Many modern-day WLAN systems today are based on IEEE specifications 802.11.
2) Storage-Area Network (SAN)
A Storage Area Network is a form of network that allows for centralized data storage at block-level. It is used mostly for producing storage tools, such as disk racks, digital jukeboxes, and tape libraries.
Also, See SAN and NAS Storage | How they work?
3) System-Area Network
A virtual network is used by the system region network. It provides high-speed connectivity in applications from server to server and from processor to device. The processors connecting to a SAN network run at relatively high speed as a single device.
4) Passive Optical Local Area Network
POLAN is a networking platform that allows you to fit in the cabling framework. It helps you to address problems related to enabling Ethernet protocols and network programs.
POLAN enables you to use an optical splitter to isolate an optical signal from an optical fiber in a single mode. This single signal is translated into several signals.
5) Home Area Network (HAN):
A Home Area Network is often designed to create a local area network (LAN) inside the household utilizing two or more linked computers. Of starters, around 15 million households in the United States have more than one device.
This kind of network lets owners of machines interconnect with other devices. This network enables data, applications, printers, and other peripherals to be exchanged.
6) Enterprise Private Network :
Enterprise private network (EPN) networks are developed and operated by organizations wishing to safely link multiple locations and access specific computing resources.
7) Campus Area Network (CAN):
A Campus Area Network comprises interconnecting LANs within a specified geographic region. A university college, for example, may be linked to several school buildings that serve all the academic divisions.
8) Virtual Private Network:
A VPN is a private network that connects remote sites or users, using a public network. The VPN network uses “virtual” connections that are routed to the remote site via the internet from the private network of the enterprise or a third-party VPN service.
It’s a free or charged service that makes your web surfing over public WiFi hotspots safe and confidential.
Network Topology Type: bus, loop, circle, grid, node, hybrid, P2P
What is Topology?
Network topologies define the methods for mapping all of the elements of a network. The term topology applies both to the physical and logical network structure.
We should clarify in this Network topology tutorial:
Types of Networking Topologies
Two main types of networking topologies are 1) Physical topology 2) Logical topology
Physical topology:
This type of network is an actual layout of the computer cables and other network devices
Logical topology:
Logical topology gives insight’s about the network’s physical design.
Different types of Physical Topologies are:
- P2P Topology
- Bus Topology
- Ring Topology
- Star Topology
- Tree Topology
- Mesh Topology
- Hybrid Topology
Point to Point
Point-to-point topology is the simplest of all topologies within the network. The network in this system consists of a direct link between two computers.
Advantages:
- This is quicker and more secure than certain forms of communication since a clear link occurs.
- Any network operating system requires
- Requires no expensive server because individual workstations are used to access the data
- There is no need for dedicated network technicians as each user sets their permissions
Disadvantages:
- The biggest drawback is that it is used only for small areas where machines are connected.
- You can’t centrally back up data and directories
- Aside from the permissions, there is no protection. Many people don’t need to sign in to their workstations.
Bus Topology
Bus topology uses a single cable that links all the nodes it holds. The central cable serves as a conduit of the entire network. Each of the networked machines serves as the controller of the machine. It is regarded as a linear bus topology because it has two endpoints.
Advantages:
Here are pros/benefits of using a bus topology:
- Popular for the LAN network, since it is cheap and simple to mount.
- It is commonly used when a low, easy, or temporary network installation is needed.
- It’s one of the passive topologies. But machines on the bus listen only to the data being submitted and is not liable for transferring the data from one device to another.
Disadvantages:
Here are the cons/drawbacks of bus topology:
- If the raising cable fails then the entire device crashes.
- When network traffic is high, collisions inside the network occur.
- Whenever network traffic is high, or nodes are too many, the network’s response period decreases dramatically.
Ring Topology
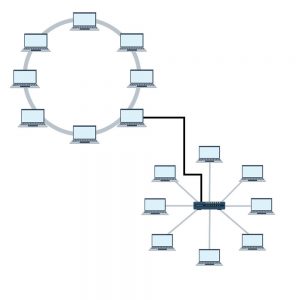
For connectivity purposes, a system has exactly two neighboring devices in a ring network. It is considered a topology of the sphere since its structure is like a triangle. Any machine in this topology is linked to a separate device. The last node, here, is merged with the first.
Using this topology, token transfers knowledge from one device to another. In this topology, all messages pass in the same direction around a triangle.
Advantages:
Here are pros/benefits of ring topology:
- Easy to install and reconfigure.
- The inclusion or elimination of an in-ring topology system demands that you only transfer two links.
- In a ring topology, the method of troubleshooting is complicated.
- One-computer malfunction will interrupt the whole network.
Disadvantages:
Here are drawbacks/cons of ring topology:
- A split in a single ring will threaten the whole network breaking down
- High-speed LANs of modern days make the topology less common.
- At all times topology signals flow in the loop, which results in excessive power consumption.
- Troubleshooting the ring network is very challenging.
- Network operation can be interrupted by connecting or withdrawing the machines.
Star Topology
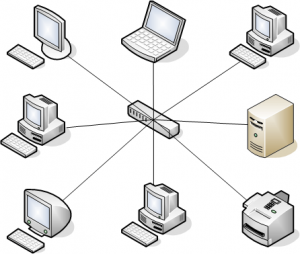
All the computers bind with the help of a center in a star topology. This cable is considered a central node, so it links the other nodes via this central node. It is most common on LAN networks, as it is cheap and simple to install.
Advantages:
Here are pros/benefits of start topology:
- Simple to patch, customize, and change.
- Only those nodes, who have broken, are impacted. Many nodes also operate.
- Good output with few nodes and very low traffic across the network.
- Through Star topology, the instruments are easy to add, uninstall, and pass.
Disadvantages:
Here are cons/drawbacks of using Star:
- If the core or concentrator fails, the nodes that are connected are disabled.
- The expense of start topology installation is high.
- Often heavy traffic on the network will delay the bus considerably.
- Output relies on the efficiency of the center
Mesh Topology
The mesh topology has a special network architecture, in which each network device links to each other. It provides a Point-to-Point (P2P) link for all network users. This provides a large degree of reliability, which ensures that even though one network cable fails, data also has an alternate way to meet its goal.
Advantages:
Here, are pros/benefits of Mesh topology
- Will extend the network without affecting existing users.
- Compared with other LAN topologies, it required additional functionality.
- P2P connections promote the process of isolation of fault detection.
Disadvantages:
- The configuration is complicated, as each node is linked to each node.
- Dedicated connections help to get rid of the traffic issue.
- Since more cables are needed it is costly. No effective usage of the networks.
Tree Topology
Tree topologies have a root node, and all other nodes which form a hierarchy are linked. Therefore, it’s often called hierarchical topology. This topology combines various topologies of stars in a single-vehicle, and it is regarded as a topology of the Star Vehicle. Tree topology is a very popular network that resembles a topology of bus and stars.
Advantages:
Here are pros/benefits of tree topology:
- One-node loss rarely impacts the remainder of the network.
- The expansion of nodes is both fast and simple.
- Managing and managing it is simple
Disadvantages:
Here are cons/drawback of tree topology:
- Topology is extensively cabled
- If more nodes are introduced, then it’s difficult to manage
- If the core or concentrator fails, otherwise connected nodes are disabled as well.
Hybrid Topology

Hybrid topology blends two topologies or more. You may see that in such a way that the resultant network does not show either of the typical topologies in the above design.
For eg, as you can see in the above picture, Star and P2P topology is being used in one department of an office. When two separate simple network topologies are related a hybrid topology is often generated.
Advantages:
Here, are advantages/pros using Hybrid topology:
- Gives the fastest way to detect and troubleshoot errors
- The highly efficient and scalable topology of the networks
- This is modular so you can increase the size of your network
Disadvantages:
- Hybrid topology architecture is complex
- This is one of the most complex systems
TCP / IP Model: What is Stack for TCP IP? Protocol Levels, Advantages
What is the TCP/IP Model?
TCP / IP Model lets you decide how to link a particular device to the internet, and how to move data between them. It helps when many computer networks are linked together to build a virtual network. The TCP / IP model aims to enable large distance communication.
TCP / IP stands for Internet Protocol / Communication Control System. It is designed primarily as a model to provide extremely efficient and end-to-end byte stream over an unstable internetwork.
TCP Characteristics
Here, are the essential characteristics of TCP/IP protocol
- Aid for Design Flexible
- It is quick to connect more devices to a Network.
- The network stays unchanged in TCP / IP until the source, and the destination devices have functioned correctly.
- TCP is a protocol directed to a relation.
- TCP delivers continuity and assures the data that comes out of series can be brought back in order.
- TCP allows you to enforce flow control and the sender can never overwhelm a data recipient.
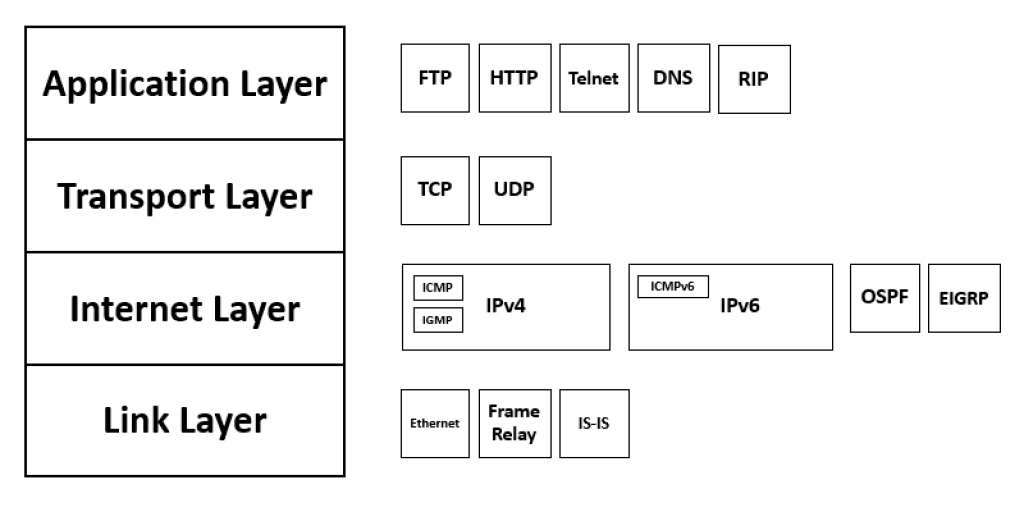
Four Layers of TCP/IP
The TCP / IP model’s configuration is split into four layers, each with different protocols.
TCP / IP is a layered structure of server architecture in which each layer is described by a particular task to execute. All of these four layers function together to transfer the data from one layer to the next.
- Application Layer
- Transport Layer
- Internet Layer
- Network Interface
Application Layer
The application layer communicates with an OSI model development system which is the highest level. The code layer is the closest OSI layer to the end-user. This ensures the OSI device framework allows consumers to communicate with certain program applications.
The application layer communicates with application software to introduce a communication component. The framework program’s understanding of the data is also beyond the reach of the OSI model.
A program, such as a file transfer, email, remote authentication, etc. is an illustration of the framework layer.
The function of the Application Layer
- Application-layer lets you define contact participants, assess the availability of services, and synchronize contacts.
- This lets users sign in to a remote host
- This layer provides various e-mail services
- This framework provides centralized database sources and permissions for knowledge of different artifacts and resources around the world.
Transport Layer
To include data transfer from a process on a source device computer to a process on a destination node, the transportation layer builds on the network layer. This is managed via single or numerous networks, and it often retains the features of reliable infrastructure.
This dictates how much data will be submitted back, at what pace, and when. Each layer builds on the notification which the framework layer gets. This will ensure that the data modules are generated in series and error-free.
The transport layer allows you to monitor a link’s reliability by flow control, error management, and segmentation or de-splitting.
The transport layer often provides an acknowledgment of the effective transfer of data and sends the next data in case of no errors. TCP is the most well-recognized transport layer proof.
The functions of Transport Layer
- It splits the message the session layer gets into fragments and numbers them to create a series.
- On the destination computer, the transport layer ensures the message is sent to the appropriate device.
- It always guarantees that the entire document arrives without error or it will be retransmitted.
Internet Layer
The second layer of the TCP / IP configuration is an internet network. That is often regarded as a component of the network. This layer’s key function is to deliver the packets from any network, and any device they still enter the destination irrespective of the path they are taking.
The Internet layer provides the practical and procedural system of moving data sequences of variable duration from one node to another with the help of various networks.
The transmission of messages at the network layer does not provide any assurance that the network layer protocol is secure.
Best Computer Networking Courses in 2020
A compiled collection of Top Software Networking Courses for students and practitioners is below. Learning networking is important for network engineers to know the problems of network design and implementation and troubleshooting. These courses include topics such as networking for full beginners, networking fundamentals, Python 3 network design, coevolutionary python neural networks, network manipulation, Wireshark, computer science, device introduction, Cisco CCNA router setup, Linux for network engineers, AWS accredited advanced networking, IP addressing, Java sockets, CCNA protection 210-260-IINS v 3.0, ne
- Introduction to networking for complete beginners
- The Complete Networking Fundamentals Course. Your CCNA start
- Networking Concepts for Beginners
- Python 3 Network Programming – Build 5 Network Applications
- Deep Learning: Convolutional Neural Networks in Python
Also, See SAP Tutorial For Beginners – What is SAP? – Step by Step Guide

